BrainTank Deep learning is a 5 week workshop that was develped designed and taught by myself, with overview and guidance from faculty at the University of Guelph’s computer science department. It was presented in October of 2021 to a class of ~20 students. The course’s goals were to:
- Minimize the barrier of entry, that plagues deep learning. We aimed to create a curriculum that gave grounded lessons about the field without advanced mathematical knowledge.
- Give students a theoretical foundation to the basic’s of working with deep learning.
- Provide students with hands-on problems that can be solved with deep learning.
- Get students up and running with the technical ability to make their own neural networks in pytorch.
Each workshop class consisted of a one hour lecture, and one hour of hands on coding time.
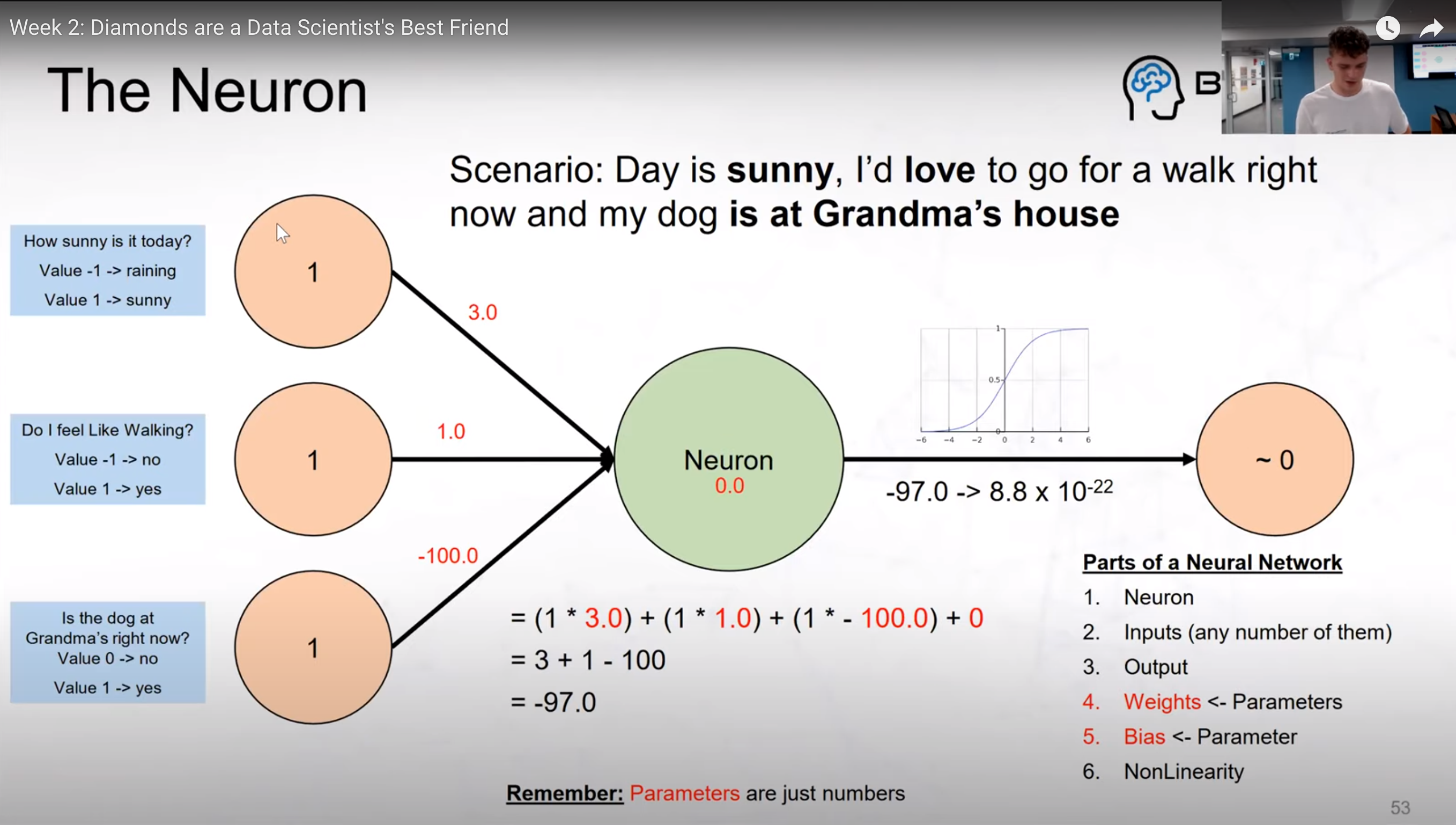
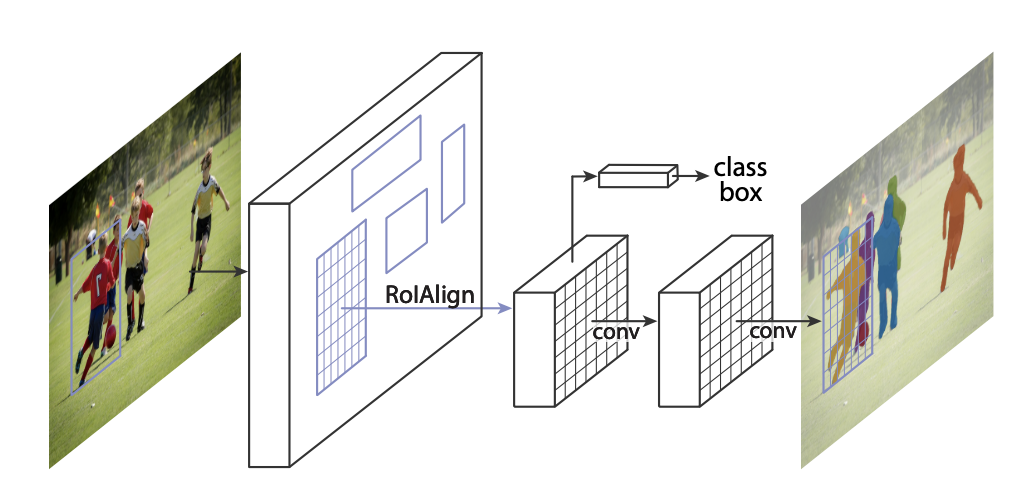
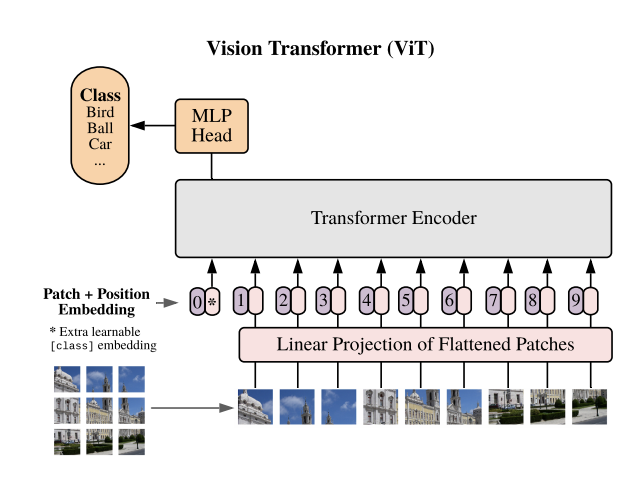
Topics covered were from using machine learning in simple linear regression, to convolutions.
The recordings of the lectures are available below.
Collaborators: University of Guelph’s Society of Computer and Information Science
Job Title: Founder
University: University of Guelph